What's That Noise?! [Ian Kallen's Weblog]
 Friday March 19, 2010
Friday March 19, 2010
Programmatic Elastic MapReduce with boto
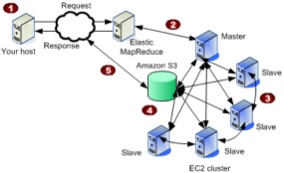 I'm working on some cloud-homed data analysis infrastructure. I may focus in the future on using the Cloudera distribution on EC2 but for now, I've been experimenting with Elastic MapReduce (EMR). I think the main advantages of using EMR are:
I'm working on some cloud-homed data analysis infrastructure. I may focus in the future on using the Cloudera distribution on EC2 but for now, I've been experimenting with Elastic MapReduce (EMR). I think the main advantages of using EMR are:
- Configuring the namenode, tasktracker and jobtracker is tedious, EMR relieves you of those duties
- Instance pool setup/teardown is tightly integrated
- Automated pool member replacement if an instance goes down
- Built in verbs like the "aggregate" reducer
- Programmatic and GUI operation
While there's a slick EMR client tool implemented in ruby, I've got a workflow of data coming in/out of S3, I'm otherwise working in Python (using an old friend boto) and so I'd prefer to keep my toolchain in that orbit. The last release of boto (v1.9b) doesn't support EMR but lo-and-behold it's in HEAD in the source tree. So if you check it out the Google Code svn repo as well as set your AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY environment variables, you can programmatically run the EMR wordcount sample like this:
from time import sleep
from datetime import datetime
from boto.emr.step import StreamingStep
from boto.emr.connection import EmrConnection
job_ts = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
emr = EmrConnection()
wc_step = StreamingStep('wc text', \
's3://elasticmapreduce/samples/wordcount/wordSplitter.py', \
'aggregate', input='s3://elasticmapreduce/samples/wordcount/input', \
output='s3://wc-test-bucket/output/%s' % job_ts)
jf_id = emr.run_jobflow('wc jobflow', 's3n://emr-debug/%s' % job_ts, \
steps=[wc_step])
while True:
jf = emr.describe_jobflow(jf_id)
print "[%s] %s" % (datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %T"), jf.state)
if jf.state == 'COMPLETED':
break
sleep(10)
Have fun hadooping!
hadoop boto python aws elasticmapreduce s3 ec2
( Mar 19 2010, 11:48:51 AM PDT ) Permalink


![Validate my RSS feed [Valid RSS]](/images/valid-rss.png)